All official European Union website addresses are in the europa.eu domain.
See all EU institutions and bodiesEU and global marine policies
The Marine Strategy Framework Directive (MSFD) builds on all the existing legal instruments for the protection of the marine environment and the sustainable development of maritime sectors, integrating their objectives into a coherent framework that contributes the achievement of the objectives of wider EU policies for environmental protection and sustainability, such as the EU Green Deal and the Biodiversity Strategy 2030.
Moreover, the MSFD is a key instrument for the fulfilment of the EU obligations in the context of the four Regional Sea Conventions (HELCOM, OSPAR, UNEP/MAP Barcelona Convention, and Bucharest Convention). This includes the joint preparation of marine environmental assessments together with non-EU states whose marine waters fall within the same marine region or subregion, helping to ensure that the MSFD assessments are coherent and coordinated.
Finally, the MSFD contributes to the achievement of the objectives of marine environmental protection set at global level, such as the Sustainable Development Goal 14 and the targets set by the Kunming-Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework in the context of the Convention on Biological Diversity.
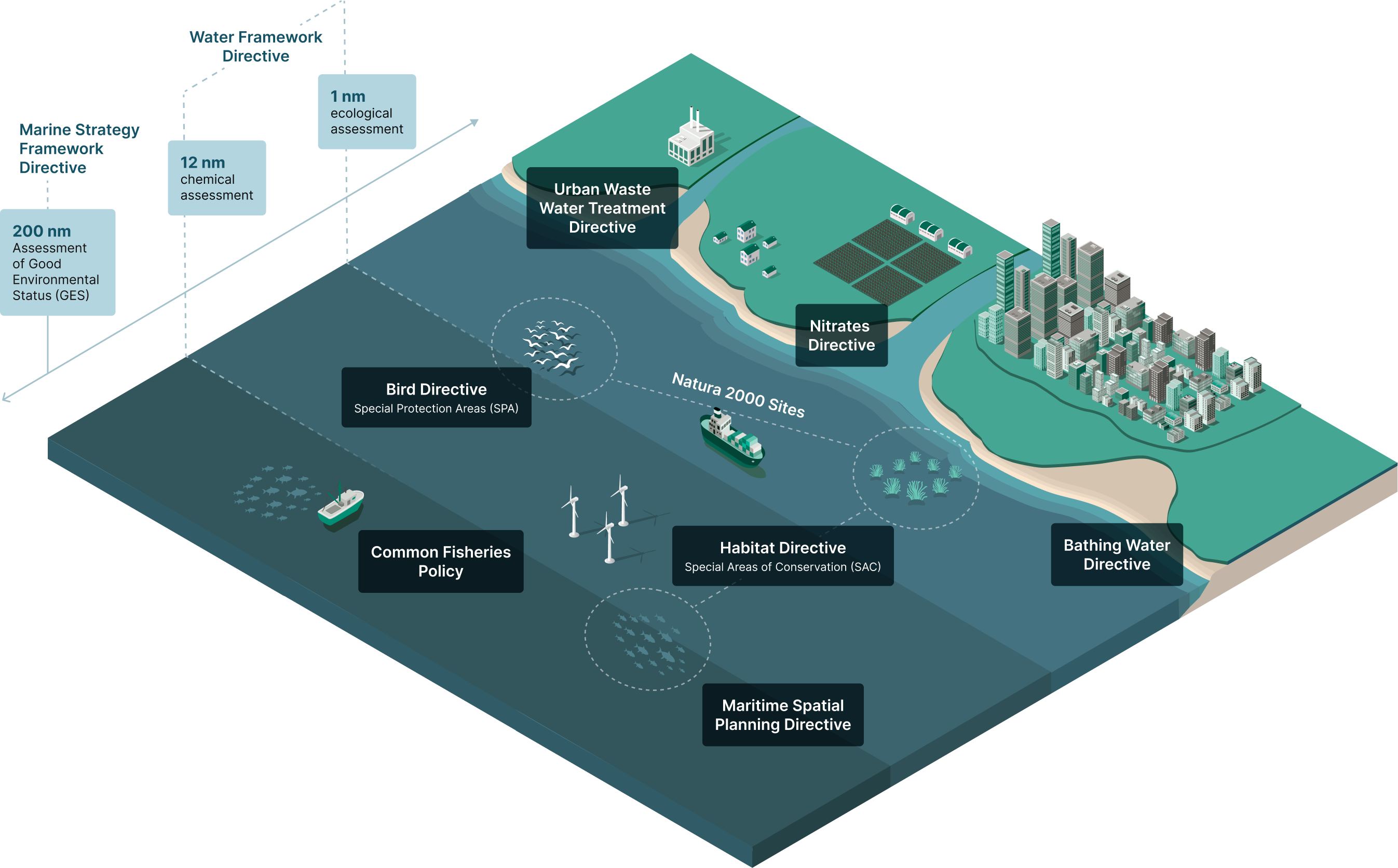
The MSFD builds on existing Directives and Regulation, developed in the course of the last decades, and extends the protection of the marine environment to include other spatial areas and ecosystems (e.g. Member States’ territorial waters), or pressures and impacts not previously addressed (e.g. underwater noise and marine litter). Simultaneously, the MSFD contributes to achieving the policy targets and objectives set in key environmental policies at EU level.
EU policy initiatives
European Green Deal
The European Green Deal is a set of policy actions set by the European Commission in 2020, which aims to tackle Europe’s most pressing climate and environmental-related challenges and make Europe the world’s first “climate-neutral bloc” by 2050. It is a new growth strategy that aims to protect, conserve and enhance the EU's natural capital, and protect the health and well-being of citizens from environment-related risks and impacts. The Green Deal commits to the achievement of specific objectives for many sectors (energy, transport, agriculture, and industry), and to protect the environment and the oceans, through the implementation of key policies such as the EU 2030 Biodiversity Strategy, the Zero Pollution Action Plan, the ‘Farm to Fork’ Strategy, the Circular Economy Action Plan, the Chemicals strategy for sustainability, the Blue Economy Strategy, the Common Fisheries Policy, and the Climate Law. The EU Green Deal fosters the full implementation of the existing environmental legislation, proposing a green EU that supports the global ambition of ensuring that all the ecosystems are restored, resilient, and adequately protected by 2050.
EU 2030 Biodiversity Strategy
The EU 2030 Biodiversity Strategy builds upon the implementation of the 2020 Biodiversity Strategy, which translated the Strategic Plan for Biodiversity of the Convention on Biological Diversity into the European framework, as well as on the Post-2020 Biodiversity Framework global discussions and the European Green Deal ambitions. It aims to step up the protection and restoration of nature and integrate biodiversity considerations into EU's overall economic growth strategy. This will be done by transforming at least 30% of Europe's land and sea areas into effectively managed protected areas, and by developing an ambitious EU Nature Restoration Plan. Thus, the implementation of the MSFD and the achievement of GES for EU’s marine waters will play a crucial role to accomplish the EU Biodiversity Strategy’s objectives.
Action plan: Protecting and restoring marine ecosystems for sustainable and resilient fisheries
Building on the EU Biodiversity Strategy for 2030 commitment to legally protect 30% of our seas, with one third being strictly protected, this Action Plan integrates fisheries considerations into the protection and restoration of marine ecosystems. It aims to contribute to getting and keeping fish stocks to sustainable levels, reduce the impact of fishing on the seabed, and minimise the impact of fisheries on sensitive species. This is done, inter alia, by strengthening the interconnectedness of the actions adopted in the context of the Common Fisheries Policy (CFP) with MSFD’s objectives and actions related to fisheries, so as to contribute to implement the obligations stemming from the international obligations stemming from the new Global Biodiversity Framework of the Convention on Biological Diversity (CBD).
The Integrated Maritime Policy
The Integrated Maritime Policy (IMP) is a holistic approach to all EU policies related to the sea. It aims to foster the sustainable development of all maritime activities and of Europe’s coastal regions, by improving the coordination of related policies and by developing cross-cutting tools. It covers the policy fields of Blue Growth, Marine data and knowledge, Maritime Spatial Planning, and Integrated maritime surveillance, and includes the preparation of sea-basin strategies for alle the seas and oceans of the union. Marine environmental protection is ensured by the MSFD, which stands as the environmental pillar of the IMP.
Common Fisheries Policy
The Common Fisheries Policy (CFP) sets out a collaborative approach to managing the EU’s shared seas regarding fisheries. It lays down rules to ensure that Europe’s fisheries are sustainable and do not damage the marine environment. The MSFD integrates this objective into the wider framework of the ecosystem approach, ensuring that “populations of all commercially-exploited fish and shellfish are within safe biological limits, exhibiting a population age and size distribution that is indicative of a healthy stock” (GES Descriptor 3).
The Zero Pollution Action Plan
The Zero Pollution Action Plan is a key deliverable of the EU Green Deal. It sets the vision of reduction of air, water and soil pollution to levels that are no longer harmful for human health and natural ecosystems. For the marine environment, this implies the reduction of waste, plastic litter at sea and microplastics released into the environment. The provisions of the MSFD related to pollution minimisation and elimination, especially in relation to contaminants in the environment and in fish and seafood, and to marine litter, are key to contribute to the achievement of these objectives.
EU Waste legislation
Several EU legal instruments regulate and limit the production and discharge of several types of waste into the environment, including the coastal and marine environment, from both land-based and marine-based sources, thus contributing to the achievement of the objective of MSFD GES Descriptor 10 (“Properties and quantities of marine litter do not cause harm to the coastal and marine environment”). The Waste Framework Directive and the Single-Use Plastics Directive require Member States to prevent and remove waste from land-based sources, especially plastics. Also, other legal instruments such as the Port Reception Facilities Directive, which ensures that waste generated on ships are returned to land and adequately managed, and the Ship-source Pollution Directive, requiring Member States to impose penalties in the event of discharges of oil or other polluting substances from ships.
Directives regulating marine-related elements
Marine Strategy Framework Directive (MSFD)
The Marine Strategy Framework Directive (MSFD) requires EU Member States to take measures to achieve and maintain Good Environmental Status (GES) in the marine environment.
This is to be achieved by developing national marine strategies, following an ecosystem-based approach, which apply to all marine waters of the Member State. The strategies have to be coherent and coordinated across each MSFD marine region or subregion, which is mostly achieved through existing mechanisms, such as the Regional Sea Conventions, or through bilateral processes.#
The implementation (and updates) of the marine strategies follows a 6-year cycle, which started in 2012 and is currently in its second phase. Articles 8, 9 and 10 are implemented during the 1st year of the cycle (2012, 2018), Article 11 is implemented during the 3rd year (2014, 2020) and Articles 13 and 14 during the 4th year (2015, 2022). The 3rd cycle of implementation will start in 2024.
Water Framework Directive (WFD)
Adopted in 2000, the Water Framework Directive (WFD) builds for the first time in the EU an integrated, ecosystem approach to achieve the good ecological and chemical status of river basin districts, including inland, transitional and coastal surface waters, and groundwater. To this purpose, the WFD establishes an iterative, six-year planning cycle, during which Member States prepare River Basin Management Plans that require the implementation of Programmes of measures. The objectives of the WFD are tightly aligned with the achievement of the GES of marine waters; they include actions to reduce marine pollution from land-based sources and to protect ecosystems in coastal and transitional waters, which are vital habitats for many marine species.
Habitats and Birds directives
The Habitats and Birds Directives are Europe’s key legislation on nature conservation. The Habitats Directive aims to achieve the Favourable Conservation Status of species and habitats of community importance, including coastal and marine sites and species, through the designation of Special Areas Conservation (SACs). In parallel, the Birds Directive aims to protect all wild bird species in the EU, including seabirds, through the creation of Special Protection Areas (SPAs). SACs and SPAs constitute the Natura 2000 network, which is the largest coordinated network of protected areas in the world. The MSFD integrates and extends the objectives of the Habitat and Birds Directives, which focus on specific habitats and species, into GES Descriptor 1 (“Biological Diversity is maintained”). Moreover, the MSFD requires Member States to establish additional spatial protection measures and build coherent and representative networks of Marine Protected Areas, explicitly including the areas already protected under the Natura 2000 network (MSFD, Art. 13).
Maritime Spatial Planning Directive
Adopted in 2014, the Maritime Spatial Planning Directive (MSPD) establishes a framework for maritime spatial planning, aimed at the promotion of the sustainable development of maritime sectors, marine areas, and the sustainable use of marine resources (Art. 1), explicitly in line with the achievement of GES under the MSFD. The MSPD requires Member States to establish and implement maritime spatial planning (Art. 4) by applying an ecosystem-based approach and promoting the coexistence of relevant activities and uses, contributing to the sustainable development of all maritime sectors and to the preservation, protection and improvement of the environment (Art. 5). MSP aims to reduce conflicts among sectors and objectives, encourage investments, increase cross-border cooperation, and protect the environment by reducing the cumulative impact of maritime activities. To this purpose, the GES objectives under the MSFD can set the boundaries inside which maritime activities, regulated in maritime spatial plans, can safely operate. Moreover, the data generated by the MSFD monitoring programmes may provide maritime spatial plans with the information needed to assess the impact of plans on the environment and deliver an adaptive management. At the same time, maritime spatial plans under the MSPD can be support the implementation of MSFD Programmes of Measures through concise planning and prioritisation of activities (Altvater and Passarello, 2018), so as to ensure the production of ecosystem goods and services and the related societal benefits.
Bathing Water Directive
The Bathing Water Directive aims to safeguard public health and protect the aquatic environment in coastal and inland areas from pollution. It requires Members States to monitor and assess the bathing water for at least two parameters of (faecal) bacteria every year, and inform the public about bathing water quality and beach management through bathing water profiles. This Directive is the primary data source to assess the inputs of microbial pathogens to the marine environment, required under the MSFD. The measures taken under this Directive are also integrated into the MSFD Programmes of measures.
Urban Waste Water Treatment Directive
Adopted in 1991, the Urban Waste Water Treatment Directive aims to protect the environment from the adverse effects of urban waste water discharges and discharges from certain industrial sectors, by regulating their collection, treatment, and discharge into the environment. This Directive is a key instrument contributing to the achievement of GES in the context of the MSFD, as it aims to limit and regulate one of the main sources of pollution for the marine environment, especially for designated eutrophic, or potentially eutrophic Sensitive Areas, including estuaries and coastal waters.
Nitrates Directive
The Nitrates Directive (1991) aims to reduce and prevent ground and surface water pollution caused by nitrates from agricultural sources, including by promoting the use of good farming practices and adopting Action Programmes. This Directive forms an integral part of the WFD framework; it contributes to limit and regulate the discharges of nutrients from agricultural sources through river basins in coastal waters, thus contributing to the achievement of MSFD GES Descriptor 5 on Eutrophication (“Human-induced eutrophication is minimised, especially adverse effects thereof, such as losses in biodiversity, ecosystem degradation, harmful algae blooms and oxygen deficiency in bottom waters”).
The global and regional commitments
United Nations Sustainable Development Goals
The Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) are the heart of the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development, adopted by all United Nations Member States in 2015. SDG 14 aims to ‘conserve and sustainably use the oceans, seas and marine resources for sustainable development’. Some of the 10 targets defined under SDG 14 are specifically addressed by the objectives of the MSFD, particularly:
- 14.1 (prevention and reduction of marine pollution of all kinds by 2025),
- 14.2 (sustainable management and protection of the marine and coastal ecosystems by 2020 to avoid significant adverse impacts, including their restoration in order to achieve “healthy and productive oceans”) and
- 14.5 (protection of at least 10% of coastal and marine areas by 2020).
In 2022, the European Union launched the “International Ocean Governance Initiative”, expressing the will to take an even more active role in international ocean governance and in implementing the UN 2030 Agenda and SDG 14. This strategy aims to strengthen the international ocean governance framework, by making oceans sustainable, safe and secure, through evidence-based decision-making. These efforts are reflected in the EU environmental legislation, especially the MSFD and its contribution to EU policies for sustainable seas and oceans.
Convention on Biological Diversity
In order to fulfil the 2050 Vision of “Living in harmony with nature”, in 2022 the Parties to the Convention on Biological Diversity (CBD) adopted the Kunming-Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework, which aims to halt and reverse biodiversity loss by 2030 by setting four goals and 23 targets, some of which are strongly related to the MSFD, such as Target 2 (at least 30% of marine and coastal ecosystems are under effective restoration), Target 3 (to protect at least 30% of marine and coastal areas), Target 4 (recovery and conservation of species and maintain and restore genetic diversity), Target 5 (sustainable, safe and legal harvesting of wild species), Target 6 (eliminate, minimise, reduce or mitigate the impacts of invasive alien species on biodiversity), and Target 7 (reduce pollution risks and their negative impacts on biodiversity and ecosystem functions and services).
Regional Sea Conventions
The MSFD requires Member States to coordinate not only with each other, but also with third countries through existing regional cooperation structures. In Europe, four Regional Sea Conventions are in place covering Europe’s marine regions and sub-regions:
(a) The Baltic Marine Environment Protection Commission (HELCOM), for the Baltic Sea;
(b) The Oslo-Paris (OSPAR) Commission for the protection of the marine environment of the North-East Atlantic Ocean;
(c) The Convention for the Protection of the Mediterranean Sea Against Pollution (Barcelona Convention) and the related UNEP Mediterranean Action Plan (UNEP/MAP); and
(d) The Convention on the Protection of the Black Sea Against Pollution (Bucharest Convention).
In this way, the actions of Member States to fulfil the obligations of the MSFD directly contribute to the achievement of the objectives of these four Regional Seas Conventions for the protection and sustainable development of the marine environment.